What is CRM?
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. CRM represents a philosophy of holistic customer orientation. A CRM system helps companies acquire new customers and maintain existing ones. Nowadays, it is essential for all companies to distinguish themselves with a distinctive customer orientation in order to survive in the market.
With the online CRM system from weclapp, you can gain new customers and retain them for the long term!
What is CRM?

There is only one boss. The customer. And he can fire everybody in the company from the chairman on down, simply by spending his money somewhere else.
Sam Walton
If you want to survive in the market, you have to think about building, maintaining and developing customer relationships. Today’s customers must be delighted and no longer just satisfied. Only then will they commit to a company in the long term and, at best, even make recommendations for that company. Many different measures lead to this satisfaction or enthusiasm, from the first contact to the follow-up. The consistent pursuit of these measures is referred to as CRM.
- tougher competitive conditions
- increasing saturation of sales markets
- greater customer sensitivity with regard to service, quality and price
- decreasing loyalty of many customers
- lays down the foundations for the use of CRM in the company
- is defined by the management of the company
- determines the scope, framework, goals and measures to be taken for CRM implementation
- encompasses all tasks involved in gathering, storing, and processing information about customers and business partners.
- Operational CRM is used in sales, marketing, and service.
What is a CRM system?
A CRM system is a software for the central management of customer information. It supports the structured collection of all customer data. Modern systems also offer the possibility of covering the entire value chain – from suppliers to partners and employees to customers.
Data, information and ultimately knowledge is the resource of the 21st century. Not only the collection of customer data and information but above all the processing of this data into knowledge, is valuable and decisive for competition. Companies should therefore make use of a modern CRM program that not only stores data and information, but also generates knowledge.
A comprehensive customer picture is a good example of this. Identifying and exploiting shopping cart analyses, cross-selling potential and buying cycles with the help of a CRM system is crucial and generates sustainable sales. The core task of such systems is therefore to support customer relationship management with IT technologies.
CRM software stores all relevant customer relationship information such as company address, contact person, contact, sales opportunities (leads), offers, orders, complaints and services. The central database thus allows flexible and combinable access across different company divisions to customer contacts, customer activities, customer appointments and contact histories.
Customer relationship management systems represent a strategically important IT application system in strongly customer-oriented companies. The importance of and demand for CRM programs have increased sharply in recent years as more and more companies discover the potential of these solutions. Modern CRM approaches also include information from social networks and customers’ Internet behavior. Furthermore, not only customers are managed, but also
- Prospective customers
- Competitor companies
- Employees
- Suppliers
- Stakeholders
This approach is also known as xRM (Extended Relationship Management).
What is necessary for the successful use of a CRM system?
The successful use of a CRM system depends heavily on whether the solution is accepted by employees from marketing, sales and service and is seen as an indispensable tool. To achieve this, the systems must be easy to use and meet the requirements of the employees.
The joy of using a system is considered a success factor. In this context, we also talk about user experience (UX). The UX is strongly influenced by the design of the user interfaces, the ease of use and the transparency of the application. Modern CRM programs therefore have
Dashboards that can be customized to the preferences of the individual user.
Processes are different in every company, so they have to be mapped individually.
Particularly in the field, the most up-to-date data must also be accessible while on the move.
What are the functions of a CRM system?
- Inquiry and quotation management
- Lead management
- Sales force management
- Creation and management of customer profiles
- Campaign planning and execution
- Marketing campaigns
- Lead generation
- Analysis of customer behavior
- Complaint and grievance handling
- Customer care and after-sales service
- Service deployment planning incl. route planning
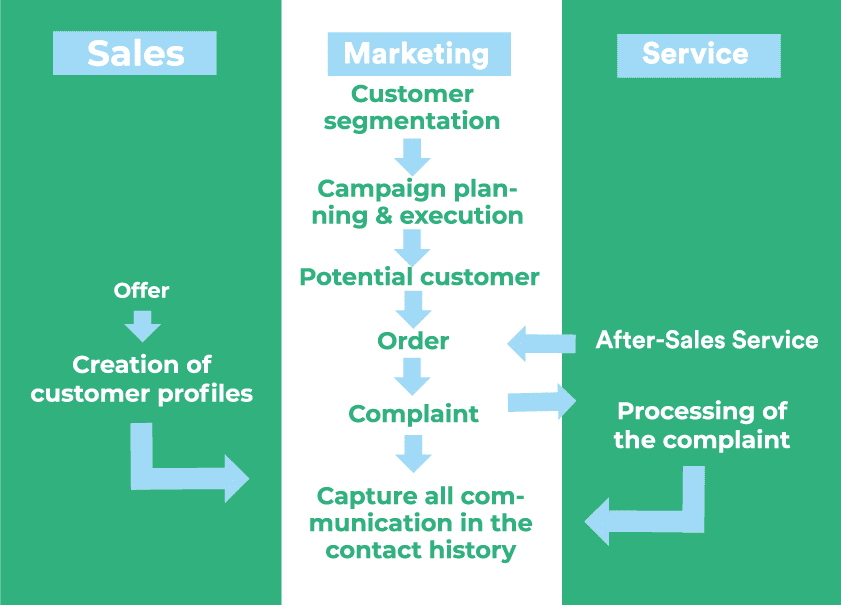
These core functions are supplemented by higher-level functions that are useful in all areas. These include, for example
- Contact management with letter, email, telephone, fax, Internet tracking
- Provision of information on mobile devices for sales employees
- Activity management, e.g. appointment reminders, resubmissions
- Document management
- Reporting and controlling in all areas
- Knowledge-oriented databases, e.g. in the service department
- Data exchange between internal and external data sources
These functional examples are fulfilled by the following 4 components of a CRM system:
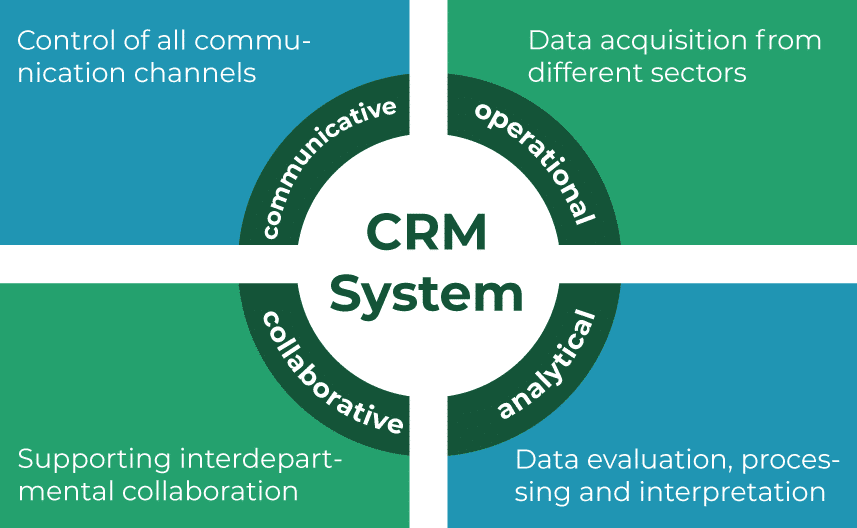
Operational CRM component
In operational CRM, the basic data is obtained from the following areas
- Sales
- Marketing
- Customer service
The sources of information can be internal or external. Typical information relates, for example, to offers, orders or complaints. This operationally acquired data, in turn, forms the basis for analytical CRM. Conversely, the results of analytical CRM form the basis for campaigns or reminder actions, e.g., for offers of operational CRM.
Analytical CRM component
The analytical part of the CRM system is where the data from operational CRM is prepared and interpreted. The evaluation is carried out using business intelligence methods. Nowadays, CRM and business intelligence must go hand in hand for optimal customer management. Exemplary reports are
- Customer evaluations (ABC analyses)
- Cross-selling opportunities
- Customer segmentation
- Offer management information
This means that in the analytical part of the CRM, the data of the operational CRM is examined in order to identify, for example, customer potential, customer behavior, and meaningful, concrete operational customer activities (e.g., campaigns).
Communicative CRM component
The focus here is on the use of various communication channels, e.g. via
- Internet
- Telephone
- SMS
- Smartphone Messenger
- By mail
In this context, the direct link to social networks is also becoming increasingly important. The communicative CRM component acts as a comprehensive interface and maps the entire contact history with a customer.
Collaborative CRM component
The focus of the collaborative component is on supporting cooperation within a company across different departments (e.g. sales, marketing, support) or even across companies by including
- customers
- Logistics partners
- suppliers
The goal is to bundle all relevant information in a central database in order to be even more competent towards the customer. The inclusion of external partners, in particular, presents a challenge, both technically due to a large number of IT interfaces and in terms of processes.
The operative, analytical, communicative and collaborative components of a CRM system support above all the areas of sales, marketing and service with competition-relevant information. This not only increases customer satisfaction but also customer loyalty, sales, profit and market share.
What is the availability of CRM systems on the market?
CRM programs differ not only in the form of their realization as stand-alone or embedded systems but also in the way they are offered on the market. Thus, the following can be distinguished:
- Commercial standard systems
- Open-source systems
- Cloud CRM systems
It is also conceivable to develop a CRM program in the form of custom software. However, this is likely to be used only in special cases or special industries and will not be considered below.
Commercial CRM standard software
Commercial CRM standard software is mainly offered as part of an ERP system (embedded system part, e.g. SAP). However, there are also a large number of standalone commercial CRM standard solutions (e.g. Oracle CRM). For such systems, license and maintenance fees for use must be paid to the manufacture. Customization or additional programming is used to adapt the systems to company-specific requirements.
Open Source CRM Software
Open source CRM systems are free of charge and the user companies can independently adapt them to their own requirements (e.g. vtiger, sugarCRM). There are no licensing or maintenance costs. However, these solutions differ only marginally in terms of setup, customization and training costs. In addition, these solutions require in-depth IT knowledge.
Cloud CRM software
A key development in recent years is software from the cloud. These solutions are referred to as SaaS solutions (Software-as-a-Service). In such cases, the provider takes care of supplying the hardware and software to operate the CRM system, as well as maintenance and updates. The only requirements for using a SaaS system are
- an Internet connection and
- a browser-enabled end device
The payment models are very flexible and usually relate to the number of users and functions used. Especially for small and medium-sized companies, it is often the fastest, most cost-effective and least risky way to integrate a CRM application system.
These are the key advantages of cloud-based CRM software:
- Short implementation times
- Low costs
- Automatic software updates
- Location and device-independent access
Which performance features should a CRM system fulfill?
First and foremost, the CRM program should fulfill the functions expected by sales, marketing and service and provide approaches for improving processes in the aforementioned areas. In other words, the CRM system must meet requirements. A powerful CRM software should have the following additional features:
The CRM software should be adaptable to different tasks. The adaptation refers to the business, the procedural (process adaptation) as well as the ergonomic (screen masks and lists) contents.
This is expressed in how high the availability is for the user. In the event of a malfunction, methods must be available to restore destroyed data sets, for example. Typical criteria for reliability are fault tolerance to operating errors, the simplicity of troubleshooting and the robustness of a system.
Modern software is available on a wide variety of devices, such as smartphones, PCs and tablets. Providers often provide free apps that allow the software to be used on the move. In this way, all employees from the various areas, such as sales or service, can access the database in real-time and also benefit from the CRM functions on-site with the customer.
Integration must exist within a CRM system. By using uniform standards, for example, data exchange between different systems should be possible.
This means that an adaptation of the CRM system, e.g. an increasing number of users, is possible easily and without major additional costs.
Internal (dialog processing) and external (printing of documents) multilingualism, so that the software can also be used globally. Mapping of country-specific features such as date formats, currencies or process requirements.
Appealing design and intuitive user guidance contribute to the acceptance of the system.
Ensuring the integrity of the program through access and egress controls and an authorization concept.
This includes, for example, the correction of program errors, improvement and expansion of functionality or adjustments to legal requirements.
Due to the storage of customer relationship information, the protection of personal data against misuse is particularly relevant. In this respect, reputable providers are characterized by corresponding certifications as well as technical and organizational measures.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a CRM system?
A CRM system generally pursues the goal of effective and efficient customer management. It is also intended to improve business processes in sales, marketing, and service through a valuable flow of information. All processes are to be aligned with the customer in order to ensure a fast and efficient response to customer concerns.
Customer Relationship Management helps companies to build strong customer relationships. CRM systems are an important tool for the realization of a CRM project in the company.
Advantages and opportunities through the use of a CRM system
- Improvement of the information flow
- Access to information from different areas
- Creation of competitive advantages through targeted information
- Increase in sales
- Retention and development of regular customers as well as effective acquisition of new customers
- Exploitation of customer potential through up- and cross-selling
- Simplify and secure delivery of sales, marketing, and service data
- Increasing the motivation of internal employees through optimized teamwork or more success
Disadvantages and risks from the use of a CRM system
However, the intensive use of customer loyalty and customer relationship measures is also associated with sales risks and disadvantages. For sustainable corporate success, the relationship between more benefits, more service, interesting additional services and special offers with discount concessions must be in a sensible ratio. Otherwise, customers will no longer pay special attention to their efforts and “free shipping” or certain discount promotions will become a matter of course.
Information about a customer’s age, place of residence, or preferences is very helpful from the company’s perspective, but it should be used thoughtfully and not inflationary in customer retention. Nevertheless, personalized and individually tailored measures represent a very good opportunity.
Difficulties in using a CRM system:
- Poor organizational integration of the CRM system
- Lack of acceptance of the system or too complex, user-unfriendly operation
- Lack of performance of the analytical and communicative CRM components
- Insufficient adaptation to operational business processes
- Poor care and maintenance of the IT technical environment
- Insufficient scalability of the CRM solution to the requirements
- Lack of consolidation mechanisms for the customer databases
- Quality of customer data is insufficient
- Partially high investments in hardware and software
It becomes clear that most of the risks and weaknesses in the use of CRM systems lie in the organizational and technical environment. Many risks can therefore be minimized or eliminated through careful planning, management and control. Despite all the technology, people play an essential role in CRM systems as decision-makers and users.
Further reading:
Stefan Helmke, Matthias Uebel, Wilhelm Dangelmaier: Effective Customer Relationship Management: Instruments – Implementation Concepts – Organization. Springer Gabler, 6th edition, 2017.- ISBN-10: 3658066237
Jörg Link: Customer relationship management: successful customer relationships through integrated information systems. Springer, 2001.-ISBN-10: 354042444X