What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing means that data is not stored locally but on remote servers. IT services and IT resources are provided via the Internet and are available in real-time. Hardware and software no longer have to be purchased and operated by the company itself but are leased. The advantages here are greater flexibility, scalability and low costs, as there is no need for a separate server structure.
Table of contents
Introduction
You think you don’t use cloud applications? You’re wrong! As soon as you have an e-mail address on the Internet and enter your user name and password, you are a user of a cloud provider. Other examples would be:
- Dropbox
- Google Drive
- Amazon Drive
- iCloud
Advantages of cloud computing
Cost saving
The use of cloud computing eliminates the need for costly investments in in-house IT infrastructures and the management of IT resources. In addition, the company saves on expensive investments in enterprise software because it only pays for the functions it actually uses. Functions are automatically updated on an ongoing basis, so that all the modules used in a cloud application are always up to date. This reduces the operating and maintenance costs for IT resources.
Location-independent scalability
Companies can promptly adapt functions to changing needs in terms of quantity and quality. Time-consuming upgrade procedures for implementing new applications are thus a thing of the past. At the same time, users can access their applications and data from anywhere in the world where an Internet connection is available. This increases their flexibility and gives them a decisive competitive advantage.
Security & availability
Data backups are performed automatically by the cloud provider. Numerous security standards and guidelines are set to protect against potential threats. A "Made in Germany" application guarantees the strictest security specifications worldwide. Likewise, high technology levels guarantee the highest possible availability of applications and data.
Productivity
Through location-independent shared access, project progress can be accelerated, workflows significantly improved, and everyone involved is always up to date through real-time updating of documents. Even small companies can use powerful functions of CRM and ERP systems through cloud computing that would not be affordable via an on-premises solution.
Cloud computing delivery models
Delivery models differ in provider- and target group-dependent deployments. The three types are public cloud, private cloud and hybrid cloud:
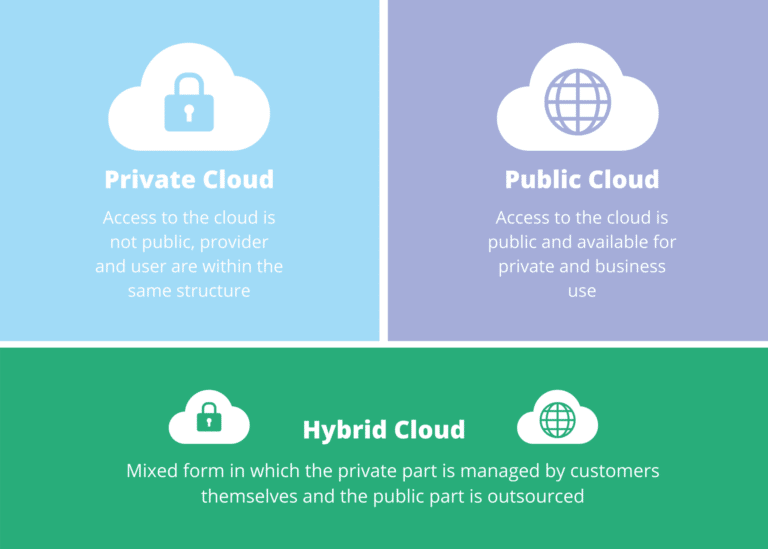
Private Cloud

In the private cloud, access is not public. Providers and users are located within the same structures or in the same environment as a company or organization. The administration of the cloud service, therefore, remains “in-house”.
Many companies opt for this form of cloud computing, which is only available to their own employees, for reasons of data protection and IT security. The difference to the classic client-server-based enterprise applications lies in the provision via the web browser, the freedom of installation and maintenance of the applications and the scalability of the IT infrastructure.
Public Cloud

In the public cloud, a provider’s offerings are available for private and business use, which are publicly accessible to everyone. As a rule, paid premium services for professional use supplement the service offerings that can be used by anyone free of charge. Public cloud offers are available from large Internet corporations such as Google, Amazon and Apple. However, free webmail services are also included, as are offers for storage space (Google Drive) and applications such as Google Docs.
Hybrid Cloud

The transitions between the public cloud and the private cloud are sometimes fluid. The hybrid cloud is one of the most widespread hybrid forms. It combines individual components of the private cloud and standard services of the public cloud. The private part is managed by the customer. The public cloud part is outsourced, i.e. in the hands of the public cloud provider. The key here is the clean separation of business processes and allocated data. Data protection-critical applications and data usually remain under the company’s own control. Other applications, where data protection is less important, run via Internet-based services, as in the public cloud.
Cloud Computing Types
In cloud computing, a distinction is made between three different cloud types: Software as a Service, Platform as a Service and Infrastructure as a Service. These are differentiated according to the depth of the outsourcing.
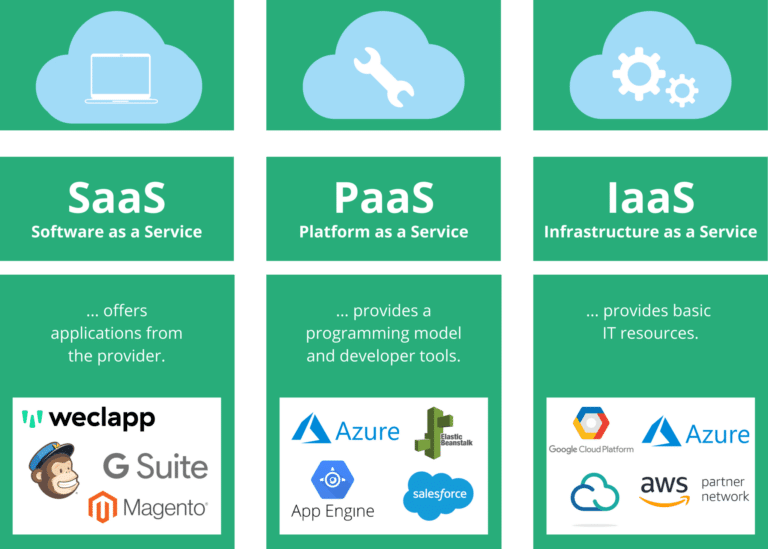
Software as a Service (SaaS)

SaaS is the most comprehensive cloud service model, ranging from the outsourcing of a single application to the outsourcing of the complete enterprise IT. Here, even the applications and the data are in the cloud and thus on the servers of the cloud provider. The user rents the software from the Internet as required as “software on demand” and also only pays for the modules actually used. This makes it very cost-effective for the user, from which it follows that this is the most commonly used software module. The range of SaaS solutions from the cloud extends from office and collaboration solutions to enterprise software for CRM and ERP such as weclapp.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)

The user of PaaS is a cloud model for system architects and application developers and has access to a development environment or framework in which they can develop and run their own applications. However, the development process itself and the programming takes place outside the company. Components in addition to IaaS is the necessary runtime environment, which includes the middleware between the operating system and the actual applications as well as the operating system. Only the applications and data storage are still managed on the company’s servers. Here, too, the computing and data capacities can be individually adapted to the needs of the company. PaaS providers include:
- Google App Engine
- Amazon Elastic Beanstalk
- Microsoft Azure
- Force.com
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS forms the base layer for all other cloud service models. Here, virtual infrastructure components (e.g., computing power, network capacity, and backup systems) can be used as needed. The computing and storage power takes place on virtualized servers and the scope can be adapted by the using company to the demand at any time. IaaS is a solution for companies that frequently have to cover peak loads (sudden high demand for power). Investing in additional IT infrastructure for this purpose would be too expensive and also saves costs for IT administration. The largest and most important players in the IaaS market currently include
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Compute Engine
- Microsoft Azure
- Alibaba Cloud
- IBM Cloud Services